Risk Management
"We continue to strengthen our risk
management across the Group by embedding
a stronger risk culture amongst our people,
articulating clearer and more specifically our
risk appetite, and institutionalising our risk
management knowledge and awareness."
Dr John Lee Hin Hock
Group Chief Risk Officer
Key Highlights
- Continued to strengthen our risk strategy and governance to embed and enhance our risk culture and management across the Group in support of our regional growth plans.
- Established a Risk Talent Management blueprint to up-skill resources and set the platform to bridge competency gaps.
- Improved our risk management processes by optimising capital and resources, improving turnaround time for credit decisions, enhancing enterprise-wide risk reporting for more effective risk oversight, and streamlining risk practices for more effectiveness and consistency across the Group.
- Implemented and initiated various risk systems enhancements such as the Risk IT Architecture roadmap, the Treasury Risk Management System and the Operational Risk Management system to ensure robust risk capabilities through technology.
Overview
During FY2012, Maybank Group made significant strides in managing its risk in a more robust and holistic manner across the Group. Amidst the challenging business landscape and tighter regulatory regime, Risk Management has managed to enhance and embed risk management into the business to drive value creation for the Group.
The risk factors faced by the Group can be categorised as follows:
Economic — Covers a range of macroeconomic risk concerns including economic environment, financial systems, infrastructure, volatility and regulation.
- The current local and global economic and market conditions will have an impact on our results.
- The Group may have direct and indirect exposures to countries with ongoing economic crises.
- We are subject to economic risks in the countries where we operate.
Geopolitical — Covers risks in areas of politics, diplomacy, conflict, crime and governance.
- Changes in the geopolitical status of the countries in which we operate and have exposures in will adversely affect us.
- We are subject to political risks and changes in diplomatic rules and governance.
Macro–prudential, Regulatory and Legal — Covers risks pertaining to changes in legislations and the regulatory landscape.
- The Group's business is subject to a wide range of legislations and regulations, as well as to regulatory and government oversight.
- Legislative or regulatory developments, or changes in the policies of regulators or governments, could have an unfavourable effect on the Group's operations, financial condition and prospects.
Environmental — Covers a range of environmental risk events such as natural disasters, irremediable pollution, and species over–exploitation.
- Exposures to companies that contribute adversely to the environment may put the Group's reputation at risk.
- There is the risk of natural disasters affecting countries in which the Group operates.
Risk in Business Operations, Governance and Internal Control Systems — Covers risks arising in the course of day–to–day business operations including breakdowns of governance and internal controls in our business processes.
- Risks concerning borrowers' credit quality are inherent in the Group's businesses.
- Operational risks are inherent in our business processes.
- Market fluctuations may reduce the value or income generation of our portfolios.
- Liquidity, or ready access to funds, is essential to the Group's activities.
- Reduction in the Group's credit rating, any subsidiaries or any of our debt securities could increase the cost or availability of funding and adversely affect our liquidity position and interest margins.
Technological — Covers risks in the area of current and emerging technologies as well as external technologically– related threats such as cyber attacks, data theft, fraud, etc.
- Our operations are highly dependent on the continued employment of information technology systems.
- Any breakdown or system failure could have a major impact on the Group's businesses.
Taking cognizance of these risks, the Group continues to plan, monitor and respond to these internal and external risk factors in an anticipative manner. This is further accomplished through the continuing implementation of the Risk Transformation Programme (RTP).
The key objective of the RTP is to redesign the current state of risk architecture, aligning the capabilities of the Group's risk function with its strategic aspirations. The RTP is aimed at enhancing our global risk management processes, increasing our ability to manage risks in all markets in which we operate, improving business responsiveness, optimising our risk-return capabilities, and acting as a market and thought leader in risk management region-wide.
Highlights of key risk achievements and measures undertaken by the Group for the financial year include the following:
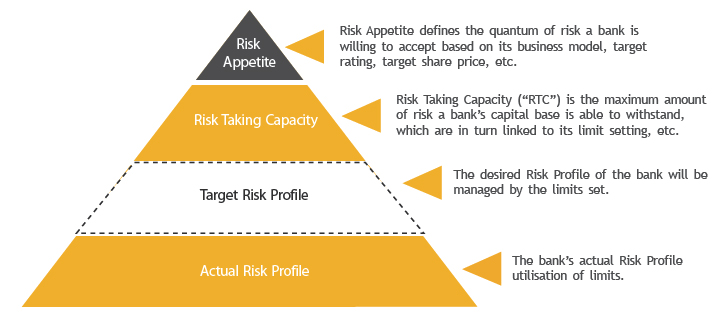
Strategy And Governance
Risk Appetite Statement
The Group's risk appetite statements have been reviewed and approved by the Board to better link our business strategies with our risk-taking capacities and to optimise our risk-return trade-offs. From Maybank's perspective, risk appetite links the risk strategy of the Group to the business strategy through desired target ratings (solvency), earnings volatility and risk limits, among others.
We have successfully implemented the Group Risk Appetite Framework across the Bank and our major overseas subsidiaries and key branches. We continue to align and embed risk appetite into our key risk management and business planning processes to ensure that our risk, return and capital are managed on an integrated basis.
For this purpose we have established a team, focused on managing the risk appetite process, to act as an interface between the Board, senior management and all the business stakeholders in the Group. We view the Risk Appetite Framework as an effective communication tool, which fosters risk-return trade-off discussions between the Board, business and risk management.
The Risk Appetite Framework communicates clearly and effectively the boundaries of risk as defined by the Board and senior management to our various businesses across the Group, and it ensures that all the Group's principal risks are considered in the business, risk management and capital planning processes.
Risk Culture
Risk Culture is defined by the Institute of International Finance (IIF) as "the norms and traditions of behaviour of individuals and of groups within an organisation which determine the way in which they identify, understand, discuss and act on the risks the organisation confronts and assumes." In line with our Board's desire to "create and embed the right risk culture", we have designed a Risk Culture Index aimed at measuring the current state of our Risk Culture across the Group.
We view Risk Culture as the foundation upon which a strong, enterprise-wide risk management framework is built. Creating and embedding a strong Risk Culture is the cornerstone of effective risk management for the Group and our clients. Therefore, through the Index, we aim to measure and target specific areas where we can focus our risk management capability-building, thus ensuring that our risk culture is institutionalised.
The Index was successfully launched in 2012, and the results will be incorporated into the performance management process across the Group. Specific action plans will also be developed to ensure that we are able to sustain our growth in a responsible and risk-aware manner.
Embedded Risk Units (ERU) Governance
During the year, the Group continued to enhance the effectiveness of the Embedded Risk Units within business sectors, overseas units and Group subsidiaries to meet the following objectives:
- To align the Group's risk management practices with leading risk management practices.
- To align the implementation of the Group's risk frameworks and policies.
- To enhance risk oversight.
- To provide clarity in the roles and responsibilities of risk management functions within business sectors, subsidiaries, overseas branches and units.
- To allocate more dedicated resources to support risk management activities.
- To improve scalability and repeatability of risk management functions in supporting the Group's regional growth.
Effective Capital Management Strategies
The Group's approach to capital management is driven by its strategic objectives and takes into account all the relevant regulatory, economic and commercial environments in which the Group operates. The Group regards having a strong capital position as essential to its business strategy and competitive position. As such, implications of the Group's capital position are taken into account by the Board and senior management before implementing major business decisions in order to preserve the Group's overall capital strength.
The Group's capital management policies are to diversify its sources of capital; to allocate and deploy capital efficiently, guided by the need to maintain a prudent relationship between available capital and the risks of its underlying businesses; and to meet the expectations of key stakeholders, including investors, regulators and rating agencies.
A set of strong governance and process guidelines is embedded in the Group Capital Management Framework. Appropriate policies are in place governing the transfer of capital within the Group. The purpose is to ensure that capital is remitted as appropriate, that it complies with local regulatory requirements, and that overall capital resources are optimised at Group and entity levels. Ultimate responsibility for the effective management of capital rests with the Board, whilst the Group EXCO is responsible for ensuring the effectiveness of the capital management policies on an ongoing basis and for updating the Group Capital Management Framework to reflect revisions and new developments.
Basel II Implementation
The implementation of Basel III in Malaysia commenced with effect from 1 January 2013 under the new Basel III rules released on 28 November 2012 by Bank Negara Malaysia. Bank Negara Malaysia's Basel III rules are broadly in line with the proposals promulgated by the Basel Committee of Banking Supervision (BCBS) in December 2010 (updated June 2011), with the exception of a few major areas, which are more stringent than those of BCBS. Despite the more stringent Basel III requirements under the local regime, the Group expects its capital position to continue to remain healthy at levels above the minimum regulatory requirements, even without the transitional arrangements.
Please refer to pages 465 to 471 in the Financial Statements book of the Annual Report 2012 for a more detailed write-up on Capital Management and the ICAAP process.
People
Risk Talent Management Blueprint
The Group developed and implemented a comprehensive risk talent management blueprint to clearly articulate core risk competencies required by Maybank's risk professionals. In addition, we defined the training curriculum to build the required risk capabilities as well as support the management of career progression pathways and succession planning.
Risk Masterclass
In our continued effort to up-skill risk management resources, our subsidiary Bank Internasional Indonesia (BII) hosted the annual Risk Masterclass, where risk subject matter experts from across the Group were engaged to share their knowledge of various risk management topics and current risk trends.
Quality of Credit Underwriting
The Group has endorsed an Internal Assessment of Core Credit Personnel (IACCP) programme. This is an on-the-job assessment process to evaluate the competency of core credit personnel, as well as the quality of the credit proposals they produce. The IACCP will help to identify individuals' areas of weakness with the aim of recommending specific credit training programmes to develop their skills and continuously improve the quality of credit underwriting.
Proceses
Risk Weighted Assets (RWAs) Optimisation
The RWAs Optimisation Programme was designed as a collaborative effort between Risk Management and business as part of our continuous capital management process. To this end, we implemented a range of initiatives, such as developing new rating models, reviewing existing models, managing stale ratings, ensuring appropriate classification of assets and enhancing collateral management information.
Credit Decision Enhancement
Credit processes were re-engineered end-to-end for different business segments, from initial marketing to loan disbursement, with an emphasis on making our credit decisions faster without increasing our risks. We deployed a Business Process Management (BPM) tool to enhance our Loan Origination System (LOS), streamlining the credit processes for better turnaround time at every touch-point.
Market Risk Management
We achieved risk diversification effect in global Value-at-Risk (VaR) computation via the upgraded Kondor Global Risk engine at all Global Market Centres.
Operational Risk Management (ORM)
In support of the Group's intention to obtain The Standardised Approach (TSA) certification for ORM, we launched various initiatives to ensure that ORM was institutionalised Groupwide. These efforts included enhancing our ORM training effectiveness, engaging and sharing knowledge with our branch network, and attesting our personnel.
Compliance Culture
Various initiatives and programmes ranging from e-Learning Solutions, Integrity Week and Group Compliance Up-skilling Programmes were put in place to institutionalise compliance culture within the Group.
Group Risk Reporting
Recognising the importance of timely and aggregated risk information, we enhanced our risk reporting processes across the Group by means of:
- Group-wide risk report standardisation and rationalisation.
- Enhancement of Enterprise Risk Dashboard (ERD) indicators and threshold settings for more meaningful analysis and incisive decision-making.
- Risk report automation to ensure quicker turnaround time in reporting.
- Early Warning System (EWS) comprising forward-looking reviews of leading key risk indicators and scenario analysis.
Systems
Risk IT Architecture (RITA)
As part of the Risk Transformation Programme, we have developed Risk IT Enterprise Architecture which defines the target state applications, data and technology infrastructure necessary to support our risk management.
RITA was initiated to enhance the risk infrastructure to (i) promote business process efficiency, (ii) align with enterprisewide infrastructure architecture, and (iii) achieve a single source of risk information, thus optimising IT infrastructure cost.
The Group has invested extensively in a range of specific technologies to further enhance its risk management capabilities. These systems include the following:
- Treasury Risk Management System (TRMS) to ensure more robust market risk oversight capabilities over our market risk.
- Risk Data Management Solution (RDMS) which is a Basel II-compliant risk weighted assets (RWA) calculation tool which measures RWAs on an aggregated basis of the various asset classes in the Group.
- Group Exposure Management System to manage the exposure limits at Group level and provide a platform to manage concentration of exposure to single borrowers.
- Maybank Operational Risk Management (ORM) system which manages the operational risks of the Group.
- Group Collateral Management System is a centralised collateral management system, which provides the solution for more efficient management of collateral information and meets specific operational and monitoring requirements under Basel II for the use of credit risk mitigation techniques, single source of collateral data for regulatory reporting and compliance, and automatic system revaluation of specific eligible collaterals.
- Credit Risk Rating Systems allow the Group to assess and measure borrowers' credit risk based on internal rating models.
- Credit Risk Data-mart (CRDM) which is a repository of credit risk data to facilitate credit risk analytics, trending, modelling, reporting, validation and stress testing requirements in an efficient and timely manner.
Risk Management Approach
In accordance to the Group's structure and regional aspirations, the Group continuously enhances its integrated risk management approach towards the effective management of enterprise-wide risks. The Group views the overall risk management process with a structured and disciplined approach to align strategies, policies, processes, people and technology with the specific purpose of evaluating all risk types in line with enhancing shareholder value.
Risk Governance Structures
Board Level Committees
Executive Level Committees
| Executive Risk Committee (ERC) | Group Operational Risk Mgt. Committee (GORMC) | Asset & Liability Mgt. Committee (ALCO) | Group Management Credit Committee (GMCC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| The ERC, GORMC, ALCO and GMCC are Executive Level Committees responsible for the management of all material risks within the Bank. The scope of ERC encompasses all risk types, whilst the GORMC caters specifically to operational risk matters. The ALCO is primarily responsible for the development and implementation of broad strategies and policies for managing the consolidated balance sheet and associated risks. The GMCC is empowered as the centralised loan approval committee for the Group. | |||
Key components of the Enterprise Risk Management framework include:
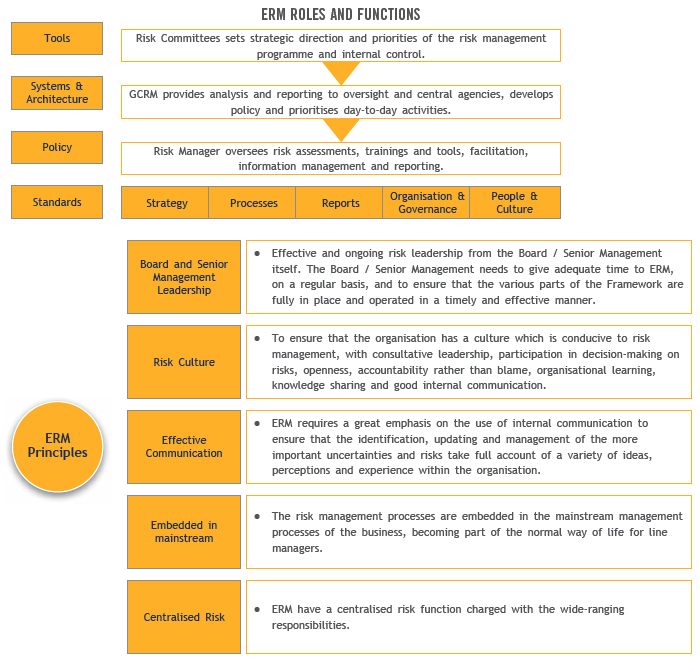
In line with its enterprise risk management approach, the Group has adopted and consistently practises Seven Broad Principles of Risk Management to ensure the integration of purpose, policy, methodology and systems across its regional footprint.
Maybank Group's Seven Broad Principles of Risk Management
The Seven Broad Principles define the key principles on accountability, independence, structure and scope.
- The risk management approach is based on three lines of defence – risk taking units, risk control units and internal audit.
- The risk taking units are responsible for the day-to-day management of risks inherent in their business activities, while the risk control units are responsible for setting up risk management frameworks and developing tools and methodologies for the identification, measurement, monitoring, control and pricing of risk. Complementing these is internal audit, which provides independent assurance of the effectiveness of the risk management approach.
- Risk management provides risk oversight for the major risk categories including credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, operational risk and other industry-specific risks.
- Risk management ensures that the core risk policies of the Group are consistent, sets the risk tolerance levels and facilitates the implementation of an integrated risk-adjusted measurement framework.
- Risk management is functionally and organisationally independent of the business sectors and other risk taking units within the Group.
- The Board, through the Board Risk Management Committee, maintains overall responsibility for risk oversight within the Group.
- Risk Management is responsible for the execution of various risk policies and related business decisions empowered by the Board.
Moving forward, the Group will embark on the next stage of the Risk Transformation Programme, which is to focus on enhancing and integrating risk management into the business to drive value creation for the Group as follows:

Please refer to "Basel II Pillar 3 Disclosures" for detailed disclosures and write-ups on Risk Management.




